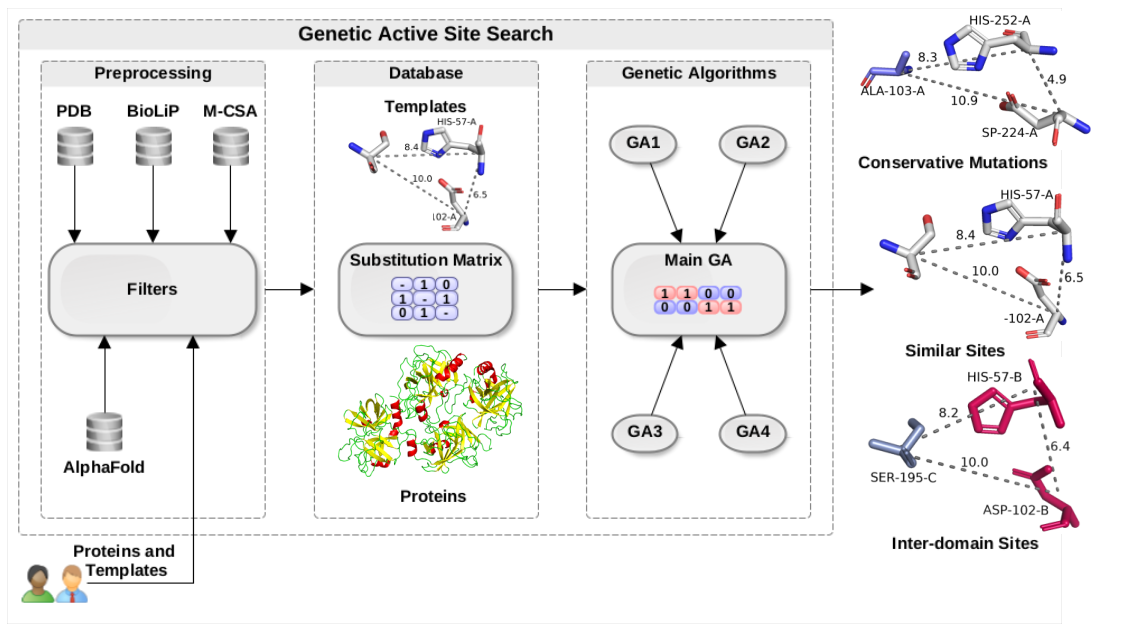
- Catalytic Site Search: Given a PDB file, performs catalytic sites search using literature-derived templates from M-CSA.
- Binding Sites Search: Given a PDB file, performs binding sites search using literature-derived templates from M-CSA.
- One-to-one Site Search: Given a PDB file, performs a search using a user-provided template.

1 COIN BITCOIN
BITCOIN PURCHASE SCAM EMAIL
Vinícius A Paiva, Murillo V Mendonça, Sabrina A Silveira, David B Ascher, Douglas E V Pires, Sandro C Izidoro, GASS-Metal: identifying metal-binding sites on protein structures using genetic algorithms, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2022;, bbac178, https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbac178
João P. A. Moraes, Gisele L. Pappa, Douglas E. V. Pires, Sandro C. Izidoro, GASS-WEB: a web server for identifying enzyme active sites based on genetic algorithms, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 45, Issue W1, 3 July 2017, Pages W315–W319, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx337
Sandro C. Izidoro, Anisio M. Lacerda, Gisele L. Pappa, MeGASS: Multi-Objective Genetic Active Site Search. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference - GECCO 2015, Madrid, Spain, https://doi.org/10.1145/2739482.2768436
Sandro C. Izidoro, Raquel C. de Melo-Minardi, Gisele L. Pappa, GASS: identifying enzyme active sites with genetic algorithms, Bioinformatics, Volume 31, Issue 6, 15 March 2015, Pages 864–870, https://doi.org/10.1093/ bioinformatics/btu746